Free Live Master Training with Dr. Shefali Tsabary⚡ 5/5/24
Your Guide to Parenting
through the Adolescent Years
BLOOM is an All-In-One Parenting Solution with On-Demand Workshops, 1:1 Coaching, Live Virtual Events & Supportive Community
In Collaboration With











BLOOM Helps You Overcome the Challenges of Raising Adolescents (8-18yrs old)
Parenting in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world presents a myriad of challenges. From navigating school pressures to managing digital distractions and peer influences, the list seems endless. It’s natural to feel overwhelmed and wonder if you’re doing enough for your children.
We provide you with the tools to understand your child better, foster open and effective communication, and build a strong, trusting relationship that lasts a lifetime. Dive into a world of expert insights, interactive workshops, and a supportive community that empowers both you and your child.
BLOOM Solutions for Parents Like You

Professional Therapy for Teens
Expert Guidance On All Topics
Fostering Open Communication
Forming Positive Relationships
Navigating Conflict and Social Challenges
Supporting Mental Health
Creating Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Achieving Academic Success
Promoting Digital Balance
Finding Purpose and Direction
Get Expert Support & Accountability that Feels Like Family
- Healthy Mind
- Healthy Body
- Puberty
- Relationships
- Gender Identity & Sexual Orientation
- Digital Life
- Sexual Health























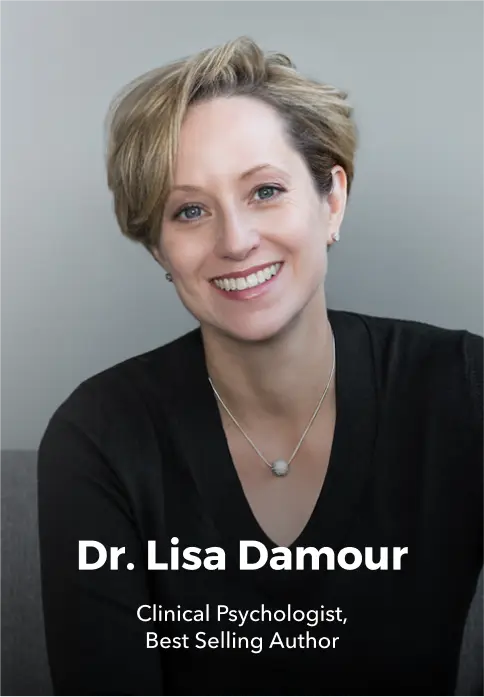






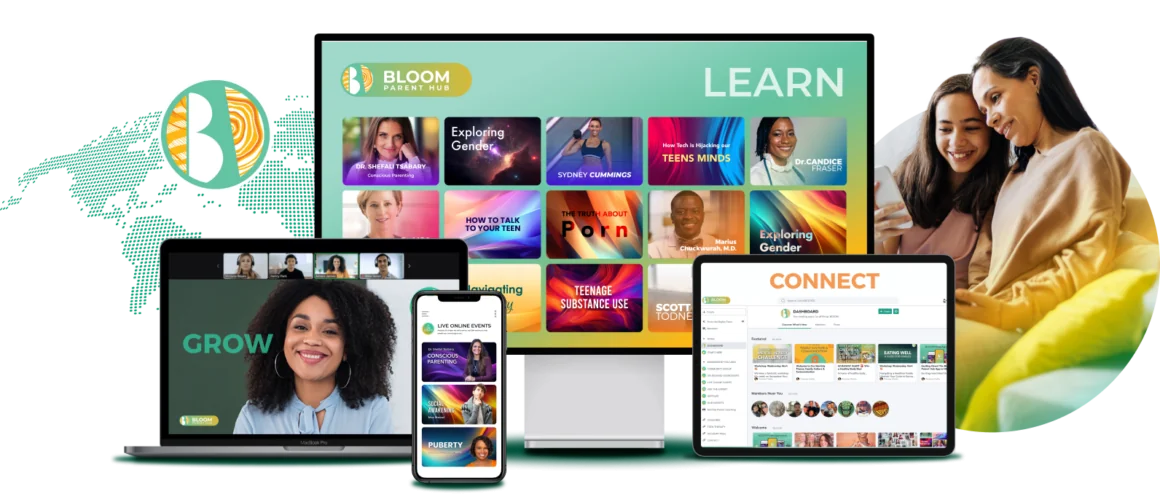
Here’s Everything BLOOM Offers


1. All-in-One Parenting Platform
2. Quarterly Master Trainings
Step into our world of exclusive live virtual master trainings where industry-leading experts delve into the most relevant topics in adolescent health & wellness. Your chance to connect directly with industry leaders and get live answers to your burning questions. ($400 Value)
3. Monthly Group Coaching
Each month, you’ll have the opportunity to receive personalized guidance tailored to your family’s unique challenges during live sessions led by our master coaches, trained by Dr. Shefali—endorsed by Oprah for her groundbreaking work in conscious parenting. ($1,200 Value)

4. Professional Therapy for Teens
Get access to one month of professional therapy for your teen on the world’s largest platform, BetterHelp. With licensed therapists available the next day, serving over 200 countries and 50+ languages, BetterHelp can help your teen navigate their unique challenges and improve access to mental health services for families. You don’t have to use it right away, but it’s there when you need it. ($300 Value)

5. Private Coaching Sessions
Elevate your parenting experience with personalized 1:1 support, guidance, and actionable strategies from our exclusive network of master coaches to help navigate the unique challenges of parenting an adolescent. ($350 Value)
Trusted by 5,000+ people

Sheila P.
I am extremely grateful to BLOOM for creating such a wonderful resource to support families. I appreciate all the trustworthy information BLOOM has complied on important topics such as puberty, digital life, and sexual health. I love that my children, partner, and I can all explore these topics at our own pace then check in with each other regularly to discuss what we’ve learned. BLOOM has already helped our family navigate some potentially awkward topics as smoothly as possible and I’m thankful to have BLOOM as a support to my kids and I for years to come.
Boston, MA

Meah S.
Out of nowhere, my daughter’s puberty “attitude” caught me off guard. Dealing with my 12-year-old, who had always been open and sweet, became a constant source of frustration. I found myself getting angry and taking her remarks personally. That’s when I discovered BLOOM – it was a game-changer. Not only did it help me understand this stage, but it also brought my daughter and me closer in a way I never thought possible. Now, our conversations are fun and light-hearted, and it’s like I’ve got my old kid back. The best part? I was able to share the Teen BLOOM platform with my daughter so that she had her own safe space that I trusted would help her understand her mind and body better.
Los Angeles, CA

Krista S.
The ease of the experience, quality and expertise of the information, and guidance in all aspects of raising children to adults makes BLOOM my go-to when I have questions, need help, or just a little confidence. I want to know that I am doing my job as a parent to the best of my ability and giving my kids accurate and positive information as they transition through puberty and into young adults and BLOOM has been instrumental in this process.
Charleston, SC

Jamie H.
BLOOM has been an amazing resource for myself and my children. When they came to me with questions about their changing bodies, we immediately went to BLOOM. Navigating the site for information was easy and allowed for them to take quizzes and ownership of what was happening within their bodies. The videos made it easy for them to understand what was happening and what was in store for the future. This sparked some great conversation and as a parent gave me some great resources to refer to as we enter the next phase of their lives. BLOOM is an invaluable resource that will help me navigate the inevitable challenges puberty and teen life will bring.
San Diego, CA
There’s a BLOOM Parenting Solution for You
Frequently Asked Questions
BLOOM is your ultimate, comprehensive guide for successfully navigating the challenging terrain of the adolescent years. Our platform is driven by a team of leading industry experts, ensuring that you have access to the most up-to-date and authoritative guidance available.
We offer a holistic approach, bringing together modern guidance, personalized coaching, and a vibrant community support network, all conveniently housed under one roof. BLOOM is your go-to destination for everything you need to thrive as a parent during the adolescent years, providing you with the knowledge, tools, and a supportive community to help you and your family flourish. Explore our vast library of expert-curated articles, engage in on-demand workshops, participate in live events, tap into our vibrant community support network, and benefit from personalized coaching through our membership offerings.
Due to overwhelming demand and our commitment to providing personalized support, we’re currently operating on a waitlist basis. This ensures that each member that joins receives the attention and resources they deserve. Rest assured, if you sign up, your spot in the queue is reserved! Keep an eye on your inbox as we’ll notify you as soon as a space becomes available for you to join our exclusive community.
BLOOM offers support to parents as they navigate the joys and challenges of their child’s transformative journey through adolescence, beginning with the onset of puberty and extending through the crucial formative years of young adulthood. Our comprehensive guidance spans the ages of 8 to 19, ensuring that parents have a trusted ally throughout this critical stage of their child’s development.
Unlock an array of benefits with BLOOM’s membership features, ranging from essential core features to premium all-access perks tailored to your unique needs.
- On-Demand Workshops: Dive into a robust library of health and wellness workshops designed to address various aspects of parenting and the unique challenges that come with raising teens. Watch anytime, anywhere.
- Parent Community: Connect with a vibrant community of like-minded parents on the same journey. Share experiences, offer mutual support, and learn from one another in this inclusive space.
- Ask the Expert: Have burning questions about parenting your tween or teen? Our forum connects you with trained professionals who can provide evidence-based responses to your questions.
- LIVE Events: Step into our world of exclusive, premium content with group parent coaching and live virtual master trainings! Industry-leading experts will delve into the most relevant topics in adolescent health & wellness and address your questions live alongside fellow BLOOM parents.
- Professional Therapy: Access to one month of professional therapy for your teen on the world’s largest platform, BetterHelp.
- 1:1 Parent Coaching: 1:1 support, guidance, and actionable strategies from our exclusive network of master coaches
Discover a vast collection of On-Demand health & wellness workshops at BLOOM, led by world renowned adolescent health experts. Dive into these insightful sessions at your leisure, gaining actionable tools and strategies to apply right away.
BLOOM is a comprehensive resource for addressing a multitude of parenting questions and challenges. Our platform begins by offering a rich collection of curated articles authored by top experts in the field. These articles serve as a valuable starting point for parents seeking guidance.
But that’s just the beginning. Inside the BLOOM membership, you’ll unlock an exclusive and invaluable feature: “Ask the Expert.” This member-only service connects you with professionals who specialize in evidence-based parenting solutions. They stand ready to provide you with personalized tools and strategies to navigate your specific parenting challenges. It’s a one-of-a-kind resource that puts the power of professional guidance right at your fingertips.
Bloom with Us!
Get expert parenting tips delivered straight to your inbox.
Help
2023 © BLOOM™. All Rights Reserved. All information on BloomForAll.com™ is for educational purposes only. For specific medical advice, diagnoses, and treatment, consult your doctor. As an Amazon Associate BLOOM may earn an affiliate commision from qualifying store purchases.